A Comprehensive Guide to Solar Panels: Powering the Future
Solar panels are transforming the way we harness energy, offering a clean, renewable source of power that is revolutionizing industries and households worldwide. With growing concerns about climate change and rising energy costs, solar panels have become a popular solution for sustainable energy production. This comprehensive guide explores everything you need to know about solar panels, from their technology and benefits to installation and maintenance.
What Are Solar Panels?
Solar panels, also known as photovoltaic (PV) panels, are devices that convert sunlight into electricity. They are composed of numerous solar cells made from semiconductor materials like silicon, which absorb sunlight and generate an electrical current through the photovoltaic effect.
Types of Solar Panels
There are three main types of solar panels:
- Monocrystalline Solar Panels: Known for their high efficiency and sleek appearance, monocrystalline panels are made from single-crystal silicon. They are durable and perform well in low-light conditions but are typically more expensive.
- Polycrystalline Solar Panels: Made from multiple silicon crystals, these panels are less efficient than monocrystalline ones but are more affordable. They are a popular choice for residential installations.
- Thin-Film Solar Panels: Lightweight and flexible, thin-film panels are made by depositing thin layers of photovoltaic material onto a substrate. They are less efficient and have a shorter lifespan but are suitable for specific applications like portable solar systems.
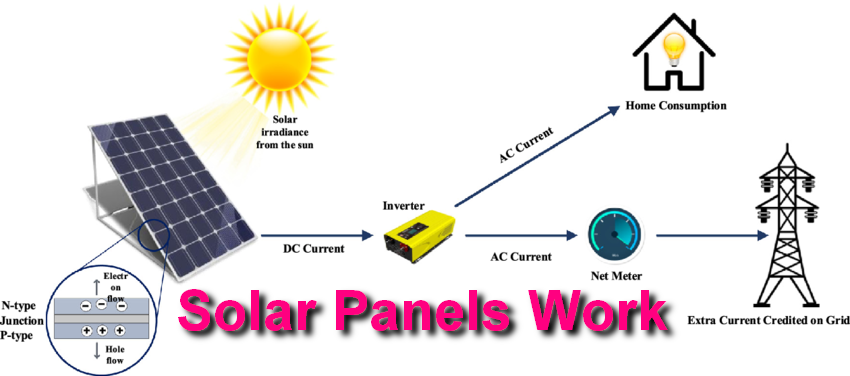
How Do Solar Panels Work?
The operation of solar panels can be broken down into three key steps:
- Absorption of Sunlight: Solar cells absorb photons from sunlight, exciting electrons in the silicon material.
- Generation of Electric Current: The movement of these excited electrons creates a flow of electricity, which is captured by conductive metal plates on the panel.
- Conversion to Usable Energy: An inverter converts the direct current (DC) electricity generated by the panels into alternating current (AC), which powers homes and businesses.
Benefits of Solar Panels
Investing in solar panels offers a wide range of benefits for individuals, businesses, and the environment:
1. Renewable Energy Source
Solar energy is inexhaustible and widely available, making it a reliable and sustainable alternative to fossil fuels.
2. Reduces Electricity Bills
By generating your own power, you can significantly reduce or even eliminate your electricity costs. Excess energy can often be sold back to the grid through net metering programs.
3. Environmentally Friendly
Solar panels produce no greenhouse gas emissions during operation, helping to combat climate change and reduce air pollution.
4. Low Maintenance Costs
Once installed, solar panels require minimal maintenance. Most systems have a lifespan of 25-30 years, with manufacturers offering long warranties.
5. Energy Independence
By generating your own power, you reduce dependence on the traditional energy grid and shield yourself from rising energy prices.
Factors to Consider Before Installing Solar Panels
1. Energy Needs
Assess your household or business’s energy consumption to determine the size and number of panels required.
2. Location and Sunlight Exposure
The efficiency of solar panels depends on the amount of sunlight they receive. Homes in regions with high solar irradiance are ideal for solar installations.
3. Roof Condition
Ensure your roof is in good condition and has sufficient space for the panels. South-facing roofs with minimal shading are optimal.
4. Budget and Financing Options
Solar panel systems can be expensive upfront, but various financing options, tax incentives, and rebates are available to offset costs.
5. Local Regulations and Permits
Check with local authorities to ensure compliance with building codes and obtain necessary permits for installation.
The Installation Process
Installing solar panels involves several steps:
- Site Assessment: A professional will evaluate your property to determine its suitability for solar panels.
- System Design: Based on your energy needs and roof structure, a customized solar system is designed.
- Permitting: Necessary permits are obtained from local authorities.
- Installation: Panels are mounted on your roof or ground and connected to an inverter and electrical system.
- Inspection and Activation: The system is inspected for compliance and activated to start generating power.

Solar Panel Maintenance
Solar panels are designed for durability, but regular maintenance can enhance their performance:
- Cleaning: Dust, dirt, and debris can reduce efficiency. Clean panels with water and a soft brush periodically.
- Inspection: Check for damage, loose connections, or shading from overgrown trees.
- Professional Servicing: Schedule annual check-ups with a qualified technician to ensure optimal performance.
Financial Incentives for Solar Panels
Governments and utilities worldwide offer incentives to promote solar adoption. Common programs include:
- Federal Tax Credits: In many countries, homeowners can claim a percentage of their solar installation costs as a tax credit.
- State and Local Rebates: Additional rebates may be available at the state or municipal level.
- Net Metering: Excess energy produced by your solar system can be fed back into the grid, earning you credits on your utility bill.
- Solar Loans and Leasing: Flexible financing options make solar installations accessible to a broader audience.
The Environmental Impact of Solar Panels
Switching to solar energy has profound environmental benefits:
- Reduction in Carbon Footprint: Solar power significantly reduces greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil fuels.
- Conservation of Resources: Solar panels use sunlight, a free and abundant resource, reducing reliance on finite resources like coal and oil.
- Decreased Water Usage: Unlike traditional power plants, solar panels require no water for electricity generation, preserving this vital resource.
The Future of Solar Panels
Advances in technology are driving the evolution of solar panels, making them more efficient, affordable, and versatile:
- Perovskite Solar Cells: These next-generation cells promise higher efficiency and lower production costs.
- Bifacial Panels: Capable of capturing sunlight from both sides, bifacial panels enhance energy generation.
- Integrated Solar Solutions: Innovations like solar roof tiles and windows are expanding the possibilities for solar energy integration.
- Energy Storage: Pairing solar panels with batteries enables energy storage for use during cloudy days or at night, increasing self-sufficiency.
Common Myths About Solar Panels
1. Solar Panels Don’t Work on Cloudy Days
While solar panels are most efficient in direct sunlight, they can still generate electricity under overcast conditions.
2. Solar Energy is Too Expensive
Costs have dropped significantly in recent years, and financial incentives make solar installations more affordable than ever.
3. Solar Panels Require Constant Maintenance
Solar panels are designed to be low-maintenance, requiring only occasional cleaning and inspections.
4. Solar Panels Harm the Environment
Though manufacturing panels involves energy use, their environmental benefits far outweigh the initial impact, making them a sustainable choice.
Conclusion
Solar panels represent a pivotal step toward a sustainable future, offering clean, renewable energy that benefits both the environment and the economy. By understanding the technology, benefits, and considerations involved, you can make informed decisions about adopting solar power for your home or business.
As innovation continues to enhance solar technology, the potential for widespread adoption grows, bringing us closer to a world powered by renewable energy. Investing in solar panels is not just a choice for today—it’s an investment in a brighter, greener tomorrow.